Hair loss can be treated in several ways. There are over-the-counter medications, hair transplants and surgery. Which one you select depends on the underlying cause as well as your personal preferences.
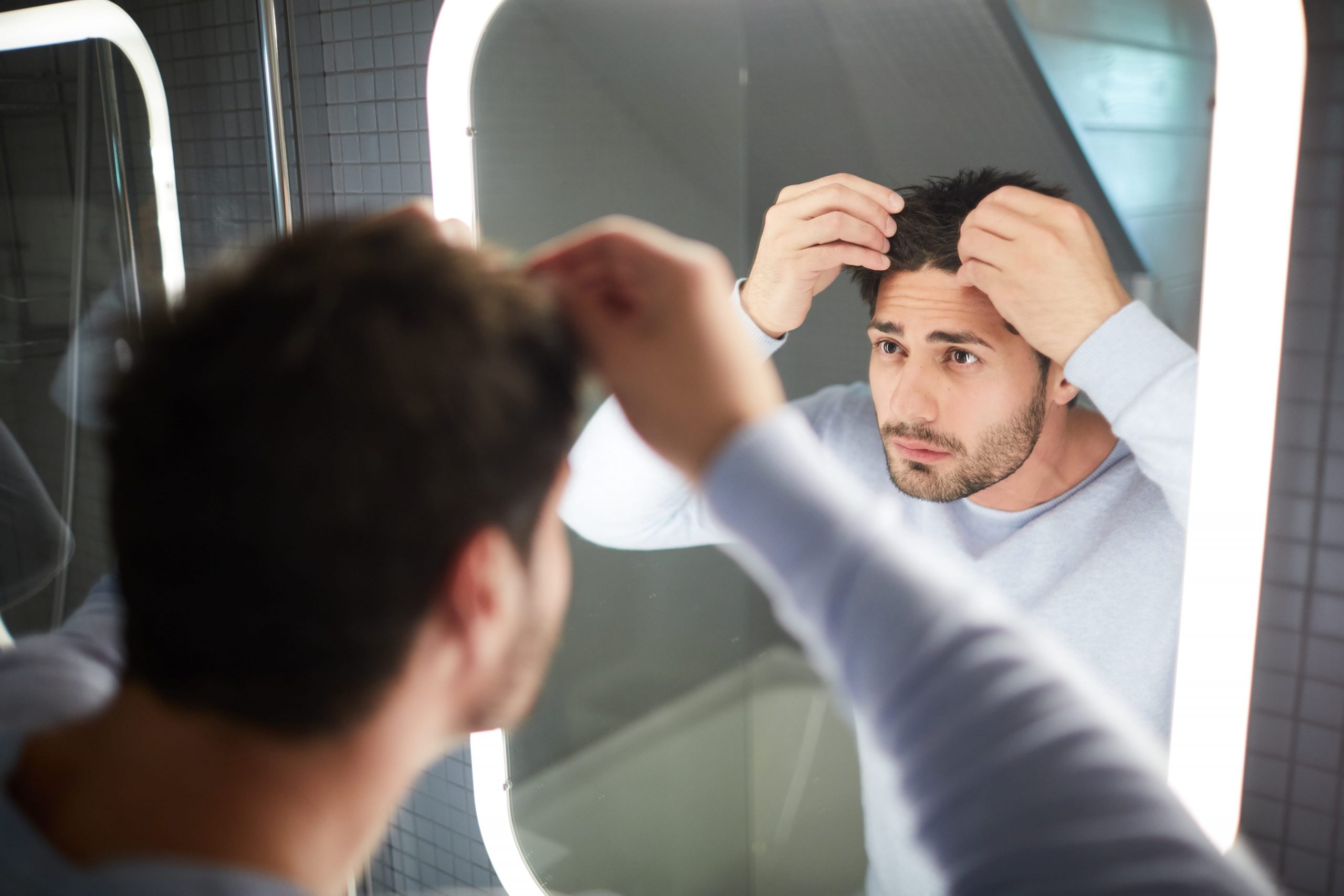
Non-scarring Baldness (Pattern Baldness): This type of hair loss is the most prevalent and may be caused by genetics or hormonal changes. Other potential causes include a diet lacking protein or iron, thyroid disorders, rapid weight loss, autoimmune diseases, stress, and certain medications.
Finasteride and minoxidil: These prescription medications have been clinically proven to be effective for treating men with thinning hair or male pattern baldness. Studies have demonstrated that these drugs slow or stop the thinning process while stimulating new hair growth.
Microneedling: Microneedling is a technique that utilizes fine needles to stimulate the stem cells of hair follicles. Studies suggest this method has more of an impact than simply applying minoxidil alone on hair growth.
PRP therapy: This procedure utilizes a centrifuge to separate blood plasma and platelets into two distinct layers that can be injected into the scalp to repair damaged blood vessels, stimulate collagen production, and encourage cell growth. Early research indicates this treatment is safe and effective for some patients.
Triamcinolone steroid injections: Injecting this steroid into the scalp can help stimulate hair growth. A doctor can administer these injections at regular intervals until your locks start growing again.
Tinea capitis: This condition, which is common among children, causes hair to fall out in patches and clumps over time. The affected areas tend to be red or scaly and itchy; they can also form sores that ooze pus. Additionally, children may have swollen glands at the back of their neck as well as a low-grade fever.
Other Types of Alopecia: Lichen planopilaris is a common skin disorder among women that causes a dry, flaky rash that covers the scalp and causes itching and hair loss.
Scalp Infections: For some people, a fungal infection of the scalp may develop which may cause hair loss. Conditions like seborrheic dermatitis, dandruff or psoriasis can all cause an outbreak of this fungus which causes itching and may produce a rash on affected areas. Left untreated, this autoimmune response attacks hair follicles and causes scarring as well as permanent hair loss if left untreated.
Cancer: Chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation treatment and a bone marrow transplant can cause hair loss due to the destruction of hair follicles in the affected area due to chemotherapy or other treatments.
Hormonal Changes: Certain hormones can cause hair to grow faster or fall out more than others, particularly for men during their reproductive years; however, this phenomenon has also been observed in women after menopause and during pregnancy.
Medications and Vitamins: Certain medications, such as some birth control pills, gout medications and high blood pressure drugs, may exacerbate or cause alopecia.